Introduction to Tokenomics
Cryptocurrency success is not guaranteed by technology alone. The long-term value of any cryptocurrency is greatly influenced by its tokenomics, or the structure of its economic system. Strong tokenomics promotes adoption, rewards participants, and ensures long-term stability.
What Is Tokenomics?
Tokenomics combines “token” and “economics.” It refers to the rules, incentives, and mechanisms that govern how a cryptocurrency functions within its ecosystem.
Key Components of Tokenomics
1. Token Supply
- Maximum supply
- Circulating supply
- Inflation or deflation mechanisms
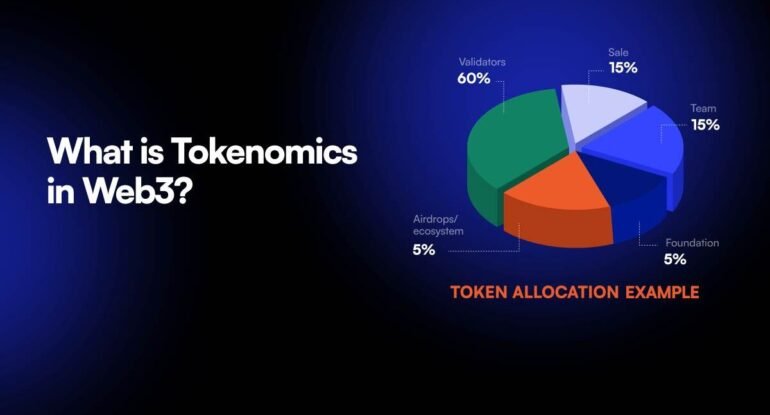
2. Distribution Model
- Public sale
- Team allocation
- Staking rewards
- Community incentives
3. Utility
Defines how the token is used within the ecosystem:
- Governance
- Payments
- Staking
- Access to services
4. Incentives & Rewards
Encourage network participation and security.
5. Governance
Token holders often participate in decision-making.
Why Tokenomics Matters
- Determines long-term value
- Prevents excessive inflation
- Aligns incentives across participants
- Encourages adoption and retention
Good vs Bad Tokenomics
| Good Tokenomics | Poor Tokenomics |
|---|---|
| Clear utility | No real use case |
| Limited supply | Unlimited inflation |
| Fair distribution | Heavy team concentration |
| Strong incentives | Weak participation |
Real-World Example
Bitcoin’s fixed supply of 21 million coins is one of the strongest examples of powerful tokenomics.
Future of Tokenomics
As DeFi and Web3 grow, tokenomics will evolve to support governance, decentralized economies, and digital ownership.
Conclusion
Understanding tokenomics helps investors evaluate project sustainability and long-term growth potential. It is one of the most important factors behind successful blockchain projects.
















